Welcome to the diabetes care clinic. If you’re reading this, you or a loved one may have been identified as being at a high risk for leg amputation due to complications arising from diabetes. This leaflet aims to provide you with essential information on the condition and guide you in its prevention and management.
Why are Diabetes Patients at Risk?
Prolonged high blood sugar levels, commonly seen in diabetes, can lead to damage in blood vessels and nerves, particularly in the legs. This damage can cause decreased sensation, poor circulation, and increased vulnerability to infections and ulcers. If not treated promptly, these complications can escalate and sometimes necessitate amputation.
Recognizing Warning Signs:
- Numbness or tingling in the feet
- Cold or discolored feet
- Non-healing sores or ulcers on the feet
- Sharp leg pains, especially at night
- Changes in the shape of the feet
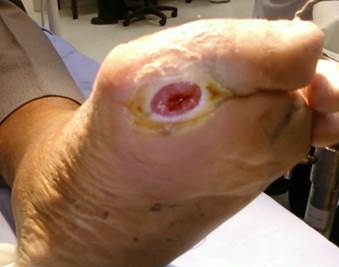
The picture shows an ulcer on the foot caused by nerve damage from diabetes
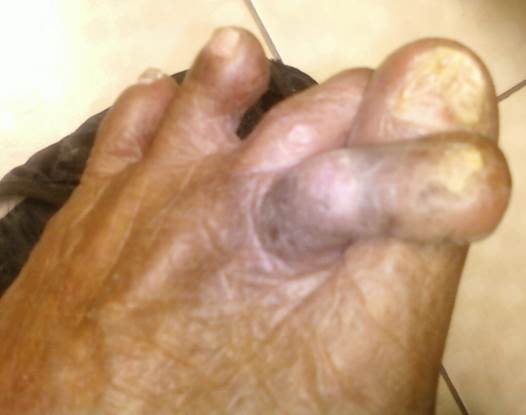
The image shows foot deformities commonly found in diabetic patients
Prevention and Care:
Regular Foot Exams: Schedule routine check-ups with your healthcare provider.
Daily Self-Inspection: Look for cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling.
Control Blood Sugar Levels: Regular monitoring and medication adherence.
Foot Hygiene: Wash feet daily, dry them gently, especially between the toes.
Moisturize: Keep your feet moisturized to prevent dry skin and cracks.
Proper Footwear: Wear well-fitted shoes; avoid going barefoot.
Avoid Smoking: It affects circulation, worsening foot health.
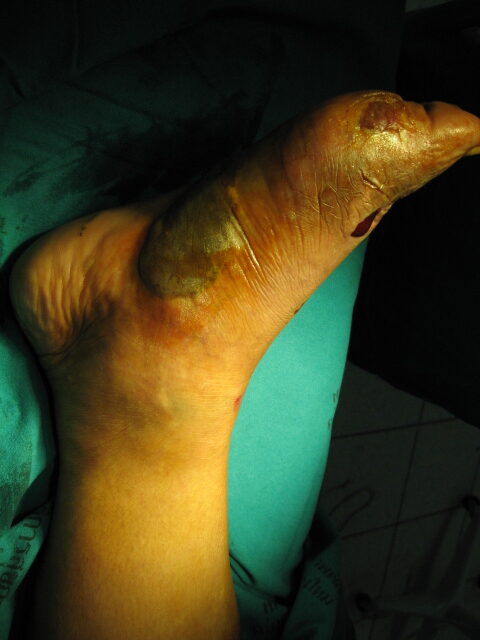
The image shows a diabetic foot with a blister, indicating a severe infection
Treatment Options:
If you’re at foot ulcer, treatments might include:
Antibiotics for infections
Wound care therapies for ulcers
Surgery to improve blood flow
In extreme cases, amputation might be considered as a last resort to prevent the spread of infection or to improve quality of life.
Post-Amputation Care (if applicable):
- Proper wound care and hygiene
- Physical therapy for mobility and strength
- Emotional and psychological support
Emotional and Psychological Impact:
It’s natural to experience a range of emotions. Seeking support from therapists, support groups, or loved ones can be beneficial.
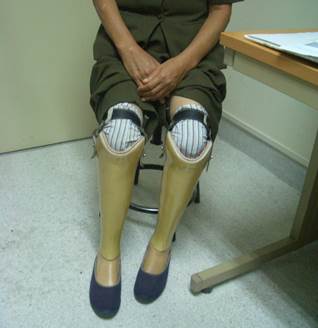
The image shows a diabetic patient who has undergone bilateral leg amputations following a severe infection.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can amputation be prevented?
Yes! In many cases, with early detection and proper care
– What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
It’s an open sore or wound commonly located on the bottom of the foot.
Remember, proactive care, regular check-ups, and immediate attention to foot problems are vital in preventing severe complications. Always consult with our clinic staff or doctors about any concerns.